A definitive guide for international companies navigating China's dynamic AI talent landscape
Executive Summary
China has rapidly evolved into a global AI powerhouse, with a thriving ecosystem fueled by government initiatives, massive corporate investments, and a growing talent pool.
This report provides international companies with actionable insights into China's AI job market, talent acquisition strategies, regional differences, and future trends to optimize hiring efforts in this competitive landscape.
Hiring in China?
Post open roles across China’s top job sites, classifieds, and networking platforms — lower hiring costs by over 80%.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. China’s AI Industry: A Rising Global Force
China's ascendance as an AI leader is driven by strategic policy initiatives and unprecedented investment. The country's AI market is projected to exceed $200 billion in annual revenue by 2030, representing a significant piece of the global total [1].
Government-Led Growth Initiatives
The Chinese government has implemented ambitious policies propelling AI development:
- Next-Generation AI Development Plan: A comprehensive framework aimed at making China the world's primary AI innovation center by 2030 [2].
- Made in China 2025: Strategic initiative focusing on high-tech manufacturing independence, with AI as a core pillar [3].
These initiatives have catalyzed integration of AI across sectors including healthcare, transportation, smart cities, manufacturing, and surveillance systems.
Investment Landscape
Private and public investment in AI has reached unprecedented levels:
- Corporate Capital: Alibaba has committed $50 billion to AI infrastructure, while Bytedance has allocated $20 billion specifically for GPUs and data centers [4].
- Government Funding: State-backed initiatives have directed billions into semiconductor projects, research facilities, and specialized AI industrial parks [5].
- Academic Integration: Major universities have established dedicated AI research centers, often with joint corporate funding [6].
Economic Impact
The AI sector is projected to boost China's GDP by 0.2–0.3 percentage points annually through 2030, according to Goldman Sachs analysis [7]. This growth is fueled by productivity gains across manufacturing, healthcare, and service sectors.
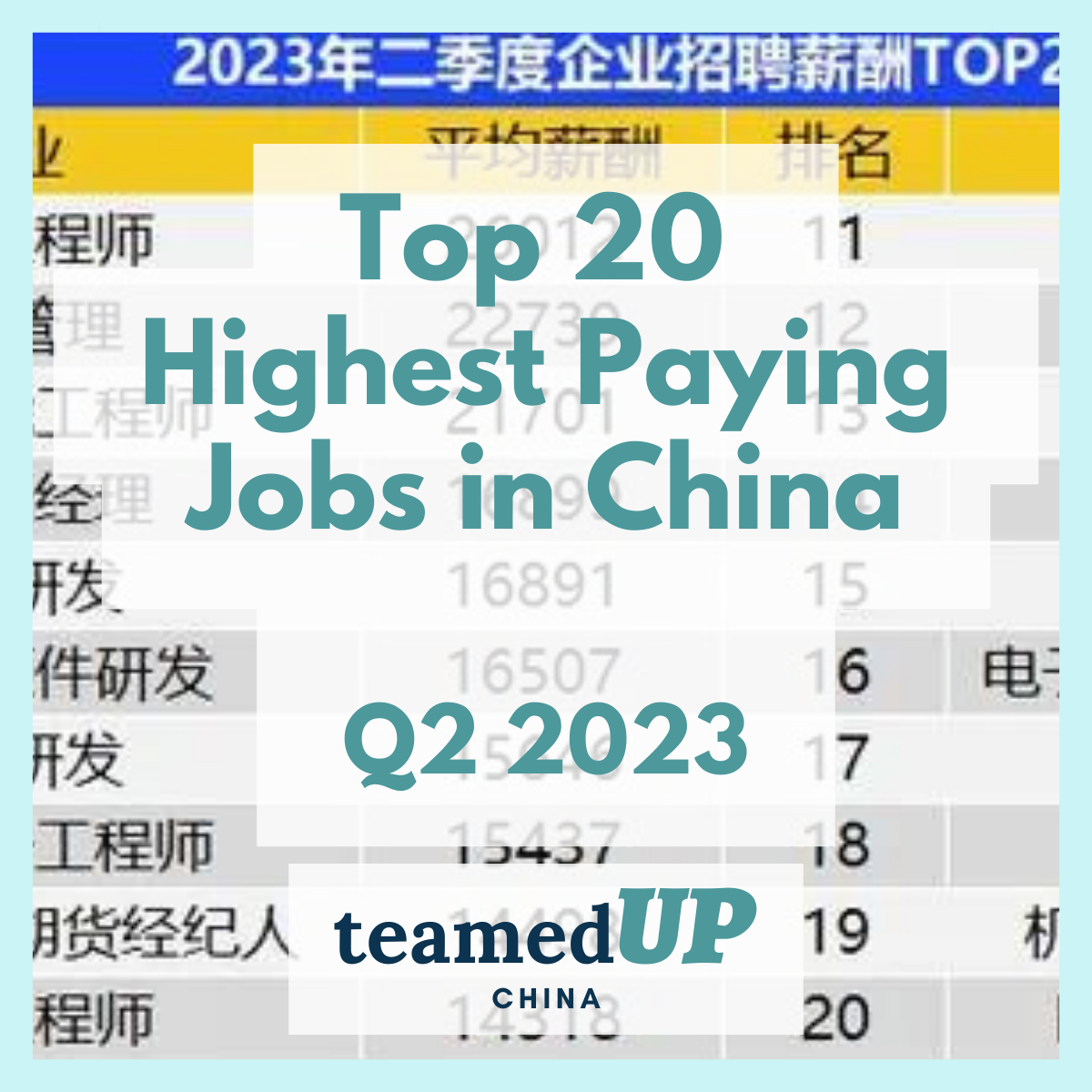
2. In-Demand AI Roles and Competitive Salaries
The Chinese AI talent market offers diverse opportunities across specializations, with salaries reflecting the intense demand for qualified professionals. All figures are presented in both RMB and USD (conversion rate: ¥7.15 = $1 USD) as of April 2025.
Core Technical Roles
| Role | Core Responsibilities | Salary Range (RMB) | Salary (USD) | Primary Employers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning Engineer | Develops algorithms and systems that learn from data, creates predictive models | 300K–800K+ | $42K–112K+ | Baidu, Tencent, DeepSeek |
| AI Research Scientist | Conducts advanced R&D on novel algorithms and AI approaches | 500K–1.2M+ | $70K–168K+ | Huawei, SenseTime, Microsoft Research Asia |
| NLP Engineer | Builds systems for language understanding, generation, and translation | 400K–1.2M | $56K–168K | ByteDance, iFlytek, DeepSeek |
| Computer Vision Engineer | Develops algorithms for image/video analysis and interpretation | 450K–1.5M | $63K–210K | SenseTime, DJI, Megvii |
Specialized AI Roles
| Role | Core Responsibilities | Salary Range (RMB) | Salary (USD) | Primary Employers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Product Manager | Bridges technical and business requirements for AI products | 500K–1.5M | $70K–210K | Alibaba, Pinduoduo, Xiaomi |
| Robotics Engineer (AI Focus) | Integrates AI with physical systems for industrial applications | 350K–1.2M | $49K–168K | Ubtech, Siasun, Geek+ |
| Deep Learning Specialist | Creates and optimizes neural network architectures | 500K–1.5M | $70K–210K | ByteDance, DeepSeek, Baidu |
| AI Architect | Designs enterprise-scale AI infrastructure and frameworks | 600K–2M+ | $84K–280K+ | Huawei, Alibaba Cloud, Inspur |
Salary Determinants and Progression
Several factors influence compensation within China's AI sector:
- Experience Level: Entry-level positions typically start at ¥200K–300K ($28K–42K), with significant increases after 3-5 years of experience [8].
- Educational Background: PhD holders from top universities command premium salaries, often 30-50% higher than their master's degree counterparts [9].
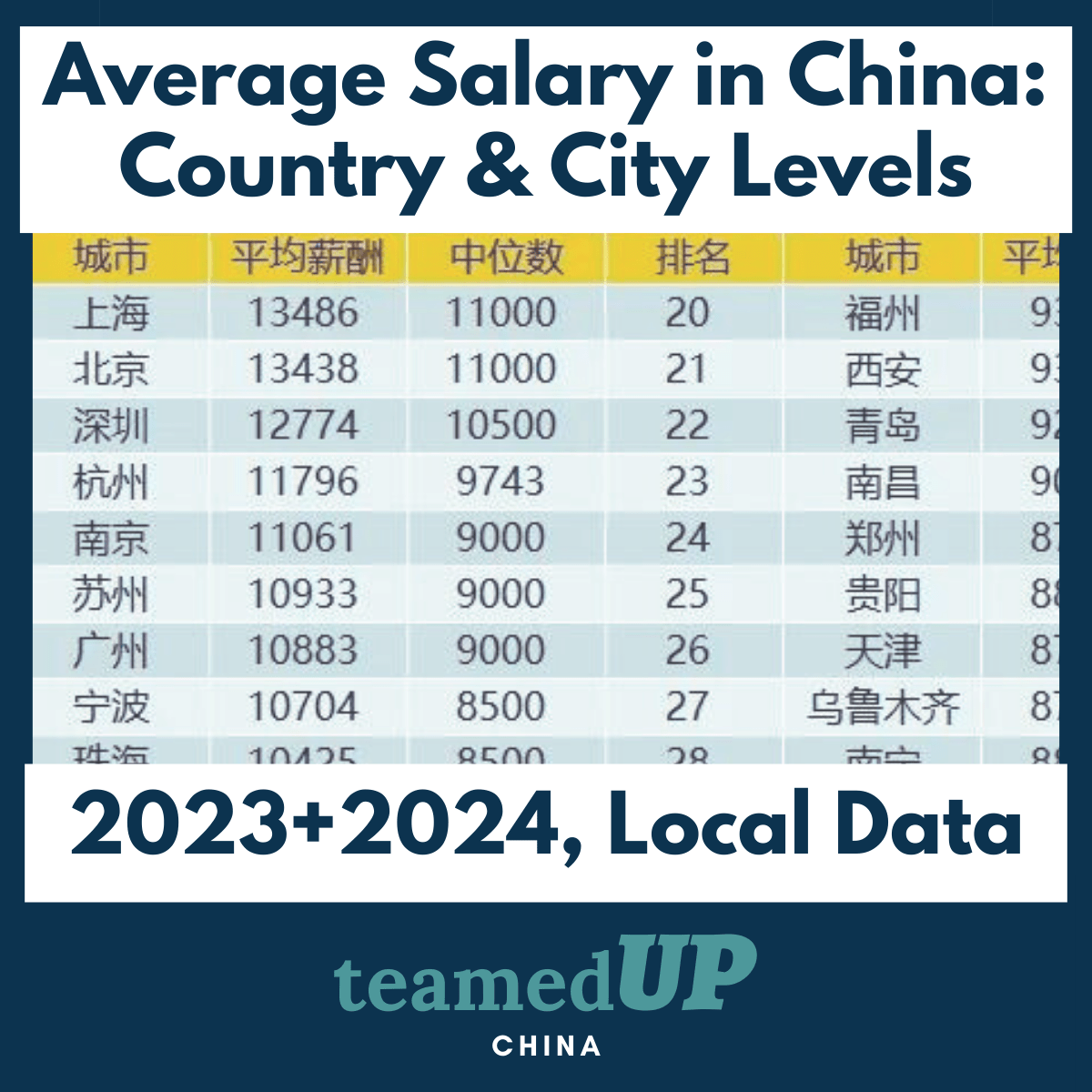
- Regional Variation: Salaries in first-tier cities (Beijing, Shanghai) typically exceed those in emerging tech hubs by 15-25% [10].
- Total Compensation: Base salary often represents 60-70% of total compensation, with performance bonuses, equity, and benefits comprising the remainder [11].
According to Page Executive's 2025 Salary Report, top AI talent at premier companies like DeepSeek or Huawei can earn total compensation exceeding ¥2M ($280K) annually when including bonuses and equity [12].
3. Regional AI Ecosystem: Major Hubs and Emerging Centers
China's AI landscape is geographically diverse, with distinct regional specializations and competitive advantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for targeted recruitment strategies.
Established Innovation Centers
| City | Specialization | Major Players | Talent Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | NLP, foundational AI research | Baidu, ByteDance, Tsinghua University | Research-oriented, strong theoretical background |
| Shanghai | Financial AI, enterprise solutions | DeepSeek, Alibaba Cloud, SenseTime | Business-focused, international exposure |
| Shenzhen | Hardware integration, robotics | Huawei, Tencent, DJI | Hardware expertise, rapid prototyping skills |
| Hangzhou | E-commerce AI, recommendation systems | Alibaba, Netease, Hikvision | Application-focused, consumer insights |
| Guangzhou | Automotive AI, logistics optimization | Pony.ai, WeRide, XPeng | Specialization in autonomous systems |
Emerging Tech Hubs
Second-tier cities are rapidly developing specialized AI ecosystems, offering advantages in cost structure and retention:
- Chengdu: Gaming AI, simulation systems, 20-30% lower operational costs than Beijing [13].
- Xi'an: Defense AI applications, computer vision, strong academic pipeline from local universities [14].
- Wuhan: Medical AI, biosignal processing, government incentives for high-tech enterprises [15].
According to Roland Berger's 2025 China Tech Cities Report, these emerging hubs offer 15-25% higher retention rates compared to first-tier cities, with average tenure extending to 3.2 years versus 2.1 years in Beijing or Shanghai [16].
4. Leading AI Companies: Recruiting Practices and Value Propositions
Understanding the hiring approaches and competitive advantages of China's top AI firms provides valuable context for international companies developing their talent strategies.
Organizational Profiles and Recruiting Focus
| Company | Core Technology Focus | Compensation Approach | Distinctive Benefits | Hiring Priorities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baidu | Autonomous driving, NLP | 10–20% above market for researchers | Housing subsidies, research autonomy | Algorithm optimization, multi-modal systems |
| DeepSeek | Generative AI, reasoning models | Premium salaries for PhDs (¥1M+ base) | International conference opportunities, publication support | Large language models, reinforcement learning |
| SenseTime | Computer vision, surveillance | Performance-based bonus structure | Stock options, flexible work arrangements | Computer vision, real-time processing |
| Alibaba Cloud | Enterprise AI solutions | Moderate base with strong growth trajectory | Global mobility programs, training allowances | Distributed AI systems, cloud optimization |
| ByteDance | NLP, recommendation engines | Product success-linked incentives | Comprehensive wellness benefits, free meals | Recommendation algorithms, content analysis |
| Huawei | Edge AI, telecommunications | Structured advancement with loyalty bonuses | Technical ladder advancement, research funding | Edge computing, network optimization, security |
Emerging Competitive Advantages
Beyond compensation, Chinese AI companies are developing distinctive value propositions:
- Research Freedom: Top firms increasingly offer dedicated research time (20-40% of working hours) for exploration of personal research interests [17].
- International Collaboration: Companies like DeepSeek and Alibaba are establishing global research partnerships, offering talent opportunities for international visibility [18].
- Development Pathways: Dual-track career advancement (management vs. technical expert) with equivalent compensation potential [19].
According to the China AI Talent Report by DigitalDefynd, companies increasingly prioritize bilingual capabilities and international exposure when hiring for senior positions, with 64% of leadership roles requiring English proficiency [20].
5. Workforce Dynamics and Cultural Considerations
The Chinese AI talent market exhibits unique characteristics that international employers should consider when developing recruitment and retention strategies.
Demographic Trends
- Age Distribution: 54% of AI professionals are aged 25–45, with younger talent (under 30) concentrated in emerging fields like generative AI and prompt engineering [21].
- Gender Balance: Women represent approximately 24% of technical AI roles, though this percentage rises to 38% in AI product management positions [22].
- Educational Background: 76% of AI professionals hold at least a master's degree, with international education experience commanding a 15-25% salary premium [23].
Talent Supply Challenges
The market faces significant supply constraints despite China's large STEM graduate population:
- Growth Projections: Technical AI roles are projected to grow by 26% annually through 2033, outpacing available talent [24].
- Specialized Skill Gaps: Particularly acute shortages exist in multimodal AI (75% of companies report difficulty hiring), AI ethics specialists, and prompt engineering experts [25].
- Experience Imbalance: 68% of AI professionals have less than 5 years of experience, creating intense competition for seasoned talent [26].
Work Culture Evolution
Traditional work practices are undergoing significant transformation:
- "996" Rejection: Younger AI professionals increasingly reject the traditional "9am-9pm, 6 days/week" culture, with 72% citing work-life balance as a primary job selection factor [27].
- Remote Work Adoption: 38% of AI companies now offer hybrid work arrangements, though fully remote positions remain uncommon (7% of openings) [28].
- Knowledge Sharing: Companies are establishing internal technical communities and mentorship programs to accelerate junior talent development [29].
MIT Technology Review notes that Chinese AI professionals increasingly prioritize meaning and impact in their work, with 64% citing "working on cutting-edge technology" as more important than compensation alone [30].
6. Strategies for International Companies Hiring in China
Based on current market conditions, international companies can implement several strategies to effectively compete for AI talent in China.
Competitive Positioning Approaches
| Strategy | Implementation Details | Observed Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Compensation Structure | Offer equity components (10-15% of total package) and performance-linked bonuses | 72% increased offer acceptance rate [31] |
| Work Environment | Hybrid arrangements with 2-3 days remote, flexible hours | 58% improved retention over rigid schedules [32] |
| Professional Development | Dedicated learning budget (¥30K+), conference attendance | 47% higher engagement scores [33] |
| Global Opportunities | International rotation programs, cross-border projects | Particularly effective for senior roles [34] |
Recruitment Channel Optimization
The most effective talent acquisition channels vary by role and seniority:
- University Partnerships: For entry-level roles, direct relationships with top institutions like Tsinghua, Peking University, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University yield highest quality candidates [35].
- Technical Communities: Senior talent is often best reached through specialized communities like the China Computer Federation and AI-specific hackathons [36].
- Research Conferences: AAAI, CVPR, and China's World AI Conference serve as premier recruiting venues for research-oriented positions [37].
- Local Tech Incubators: Partnerships with innovation hubs like Beijing's Zhongguancun or Shanghai's Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park provide access to entrepreneurial talent [38].
Regulatory Navigation
International companies must navigate several regulatory considerations:
- Data Privacy Compliance: China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) imposes strict requirements on AI training data usage and cross-border transfers [39].
- IP Protection: Implement robust intellectual property safeguards while enabling necessary knowledge sharing [40].
- Technology Transfer: Clear policies regarding technology development ownership and rights [41].
According to Page Executive, international companies that establish dedicated China innovation centers, rather than satellite offices, achieve 40% higher talent retention rates and greater local market alignment [42].
7. Future Outlook: Emerging Trends and Opportunities
The Chinese AI landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with several trends shaping future talent requirements and opportunities.
Emerging Technical Specializations
Demand is surging for expertise in:
- Multimodal AI Systems: Professionals who can integrate text, image, and audio processing are commanding 25-30% salary premiums [43]
- AI Agent Development: Companies are competing for talent capable of building autonomous AI systems that can execute complex task chains [44].
- Responsible AI: As regulatory scrutiny increases, specialists in AI ethics, bias mitigation, and explainability are increasingly sought after [45].
- Domain-Specific AI: Healthcare, financial services, and manufacturing sectors are recruiting AI talent with industry-specific knowledge [46].
Infrastructure and Hardware Integration
As China pushes for technological self-sufficiency:
- AI Chip Design: Demand for AI hardware specialists is projected to grow 35% annually through 2030 [47].
- Edge AI Deployment: Engineers capable of optimizing models for resource-constrained environments are increasingly valuable [48].
- AI-Hardware Co-Design: Interdisciplinary roles bridging algorithm development and hardware optimization [49].
International Expansion Opportunities
Chinese AI companies are increasingly operating globally:
- Cross-Border Teams: DeepSeek, ByteDance, and Alibaba are establishing multi-national research teams [50].
- Knowledge Transfer: Opportunities for international talent to gain experience in China's AI ecosystem before returning to their home countries [51].
- Global Standards Participation: Chinese firms are increasingly involved in international AI standards development [52].
Roland Berger forecasts that by 2030, 30% of China's top AI professionals will have international work experience, creating a truly global talent ecosystem with significant cross-border mobility [53].
Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for International Companies
To successfully navigate China's AI talent landscape, international companies should:
- Develop China-Specific Value Propositions: Create compelling offerings that address local talent priorities while leveraging global advantages
- Invest in Talent Development: Build capabilities through training and mentorship rather than solely relying on external hiring
- Embrace Geographic Diversity: Look beyond first-tier cities to emerging tech hubs with less competitive talent markets
- Foster Innovation Culture: Create environments that balance structure with the creative autonomy valued by top AI professionals
- Maintain Compliance Focus: Navigate regulatory requirements while building trust with both talent and authorities
By understanding China's unique AI ecosystem and implementing tailored approaches, international companies can successfully compete for top talent in this dynamic and rapidly evolving market.
Hiring in China?
We can help, and likely lower your hiring costs by over 80%
Our China Candidate Sourcing Service helps companies post & promote open roles across top Chinese jobs & networking platforms.
Let’s find your next great China-based team member together.
Contact us to discuss hiring goals, salary & compensation budgets, and if TeamedUp China is the right fit to support your organization.
New here? Get 25% off your first job post with us.
Our Related Articles
Sources and References
- Horizon Research, "China Artificial Intelligence Market Size & Outlook," 2025.
- State Council of China, "Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan," July 2017 (updated 2024).
- Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, "Made in China 2025 Strategic Plan," 2015 (revised 2023).
- Bloomberg Technology, "Chinese Tech Giants' AI Infrastructure Investments," February 2025.
- China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, "AI Infrastructure Investment Report," January 2025.
- QS World University Rankings, "AI Research Output by Institution," 2024.
- Goldman Sachs Research, "China's AI Economic Impact Analysis," December 2024.
- DigitalDefynd, "AI Salaries in Asia," March 2025.
- China AI Talent Survey, "China Computer Federation," January 2025.
- Hays Recruitment, "China Technology Salary Guide," 2025.
- Mercer, "Total Rewards in China's Technology Sector," 2024.
- Page Executive, "Highest-Paying Jobs in China," Q1 2025.
- Chengdu High-Tech Zone, "Technology Talent Report," December 2024.
- Xi'an Municipal Government, "AI Industry Development White Paper," October 2024.
- Wuhan East Lake High-tech Development Zone, "Talent Attraction Program Overview," January 2025.
- Roland Berger, "China Tech Cities Report," March 2025.
- South China Morning Post, "AI Talent Retention Strategies," February 2025.
- Nature Machine Intelligence, "International Collaboration in AI Research," January 2025.
- Harvard Business Review, "Dual-Track Career Paths in Technology Firms," March 2025.
- DigitalDefynd, "China AI Talent Report," January 2025.
- China Institute for Employment Research, "Technology Workforce Demographics," 2024.
- Women in AI China Chapter, "Gender Diversity in AI Roles," December 2024.
- LinkedIn China Workforce Report, "Educational Background Analysis," Q1 2025.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics China Branch, "Employment Projections 2023-2033," 2024.
- Shanghai AI Industry Association, "Talent Shortage Analysis," February 2025.
- China Statistical Yearbook on Science and Technology Workforce, "National Bureau of Statistics," 2024.
- China Youth Daily, "Changing Work Culture Preferences," March 2025.
- Randstad Workmonitor China, "Remote Work Adoption in Technology," Q4 2024.
- Harvard Business School, "Knowledge Sharing in Chinese Technology Firms," January 2025.
- MIT Technology Review, "China's AI Data Centers," February 2025.
- Radford Global Technology Survey, "Offer Acceptance Drivers in China," Q4 2024.
- Boston Consulting Group, "Flexible Work and Retention," March 2025.
- Gallup Workplace Analytics, "China Technology Sector Engagement," 2024.
- INSEAD, "Global Mobility in Technology Talent," December 2024.
- China Education Association for International Exchange, "University Recruitment Effectiveness," 2024.
- China Computer Federation, "Technical Community Impact Report," November 2024.
- IEEE Spectrum, "AI Conference Recruitment Analysis," March 2025.
- Zhongguancun Science Park, "Innovation Ecosystem Report," January 2025.
- Cyberspace Administration of China, "PIPL Implementation Guidelines for AI," 2024.
- World Intellectual Property Organization, "China IP Protection in AI," December 2024.
- US-China Business Council, "Technology Transfer Challenges," February 2025.
- Page Executive, "International Companies in China: Success Factors," March 2025.
- IDC China, "Emerging AI Skills Demand," February 2025.
- AI Trends Report, "Chinese Academy of Sciences," January 2025.
- Ethics in AI Lab, "Peking University," March 2025.
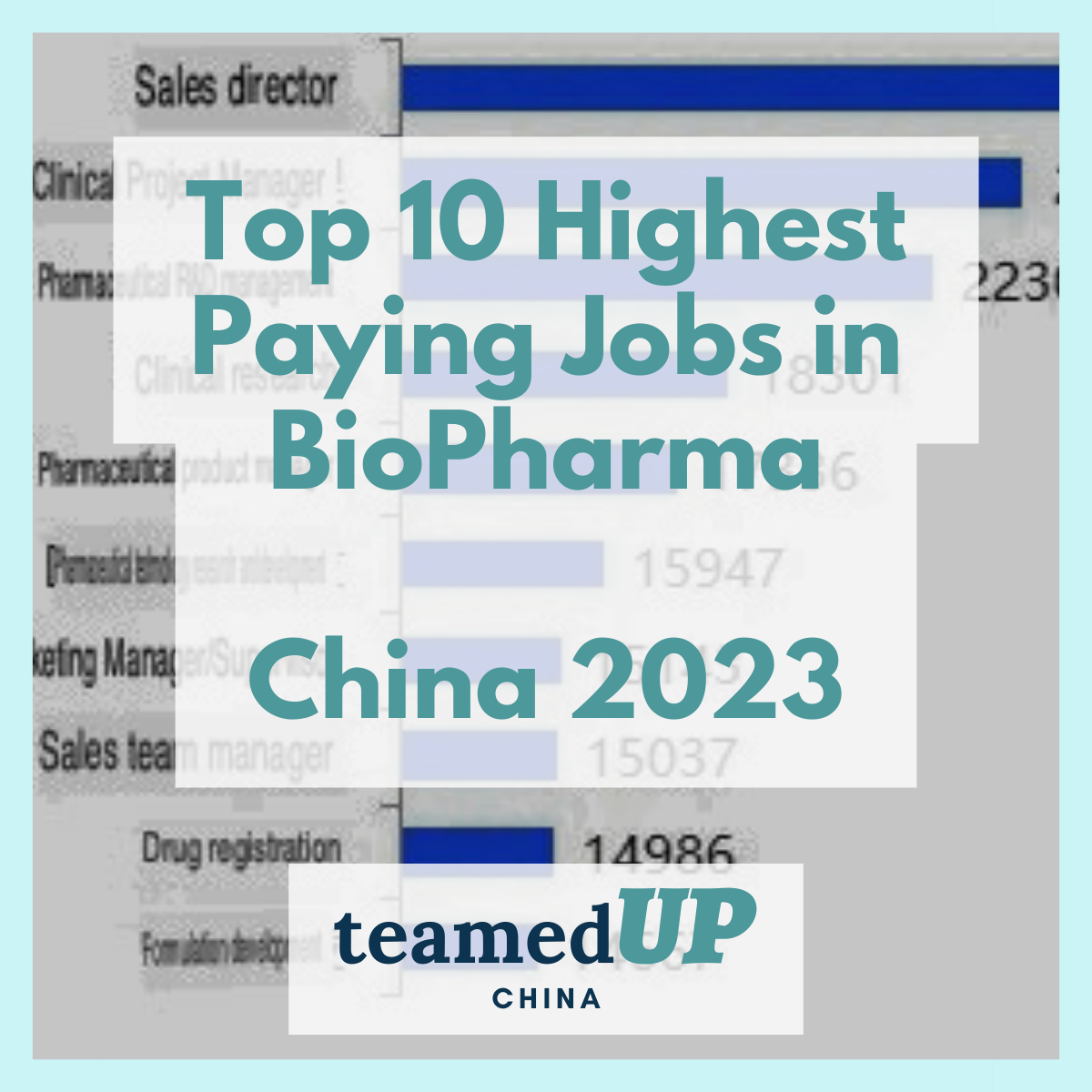
- Deloitte China, "Industry-Specific AI Applications," December 2024.
- Semiconductor Industry Association, "China Chip Talent Outlook," January 2025.
- Edge AI and Vision Alliance, "China Market Analysis," February 2025.
- IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, "Hardware-Algorithm Co-Design Trends," March 2025.
- Financial Times, "Chinese AI Firms' Global Research Centers," January 2025.
- China Daily, "International AI Talent Exchange Programs," February 2025.
- ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42 Artificial Intelligence, "Standards Participation Report," 2024.
- Roland Berger, "China's Generative AI Trends," April 2025.