China boasts the world’s largest domestic job market, yet many of its leading recruitment platforms remain relatively unknown outside the country.
These powerhouses rival global names like LinkedIn, Indeed, Monster, CareerBuilder, and ZipRecruiter in both user numbers and revenue generation. Furthermore, most of these international HR giants hardly operate in China.
So let’s dive into the biggest, most used job platforms in China!
For each platform, we’ll list:
- Company Website
- Year Founded
- Key Milestones
- User & Growth Stats
Platforms are listed alphabetically.
Table of Contents
ToggleHiring in China?
The 'Big 8' Job Platforms in China
51job (前程无忧 qiánchéng wú yōu)

Website:
Year Founded:
1998
Key Milestones:
1998: 51job’s Founding
Rick Yan and Kathleen Chien found the company, with its headquarters in Shanghai. The original goal was to provide a platform for job seekers and employers to connect online.
2004: Initial Public Offering (IPO)
In December 2004, the company went public on the NASDAQ stock exchange under the ticker symbol “JOBS.” This move helped the company raise capital to support its growth and expansion.
2005: Expansion of Regional Offices
To extend its reach across China, the organization expanded its operations by establishing regional offices in key cities like Beijing, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen. This expansion allowed the company to better serve job seekers and employers nationwide.
2006: Launch of 51job University
Launched “51job University,” an initiative to provide professional training and development programs for job seekers. This service aimed to enhance job seekers’ skills and increase their competitiveness in the job market.
2011: Acquisition of HR Solutions Provider
In October 2011 they acquired HR Solutions, a company specializing in recruitment outsourcing and human resources services. This acquisition expanded 51job’s portfolio of services, allowing it to offer a broader range of solutions to its clients.
2014: Introduction of Mobile Apps
Introduced mobile apps for iOS and Android platforms. These apps enabled job seekers to search and apply for jobs conveniently using their smartphones.
2015: Acquisition of Yingjie Sheng
In April 2015 the firm bought Yingjie Sheng, a fast-growing job and internship site focused on recent college grads.
2017: Strategic Investment in Lagou
In September 2017 the company announced that it would invest USD $120 million in Lagou to obtain a 60% stake in the company. Lagou is a leading job platform in China focused on the IT sector.
2018: Strategic Partnership with WeChat
In June 2018, the company entered into a strategic partnership with WeChat, a popular messaging and social media platform in China. This collaboration aimed to enhance the recruitment experience by integrating 51job’s services with WeChat’s extensive user base.
2022: 51job is Taken Private
‘JOBS’ is delisted from the NASDAQ through a merger with Garnet Faith Limited, in a deal valued at around USD $4.3 billion.

User and Growth Stats:
51job’s growth since launching in 1998 has been solid and steady. Since going public in 2004, the company has publicly filed key figures on their growth. Here a few of those highlights:
Annual Revenues have gone from RMB479.9 million (US$58.0 million) in 2004 to RMB4,420.4 million (US$693.7 million) in 2021, growing to nearly 11 times over!
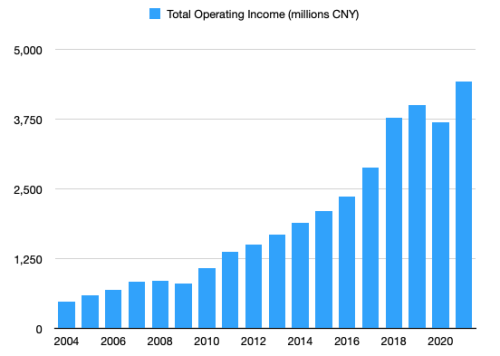
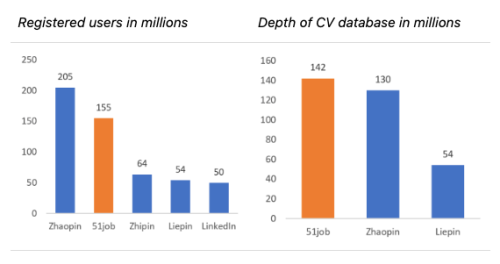
Total User Base had grown to 155 million by 2021.
Monthly Active Users (MAU) has grown to nearly 20 million as of December 2022. In comparison, global HR giant ZipRecruiter has roughly 25 million MAU.
Active CV Database had grown to over 142 million by 2020.
References and Further Info:
- Our full article on 51job: 51job (前程无忧): A Look at the Leading Chinese Job Site
- Market Screener: https://www.marketscreener.com/quote/stock/51JOB-INC-9784/news/51job-Inc-acquired-Yingjiesheng-com-for-CNY-250-million-38283555/
- Seeking Alpha: https://seekingalpha.com/article/4350254-51job-despite-short-term-pain-long-run-perspectives-look-bright
- Crunchbase: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/51job
- China News: https://www.chinanews.com.cn/cj/2017/12-20/8405156.shtml
- Paul Weiss: https://www.paulweiss.com/practices/transactional/private-equity/news/dcp-capital-acquires-china-s-51job-in-take-private-deal-valued-at-43-billion?id=43047
- PRNewswire: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/51job-inc-announces-the-establishment-of-51job-university-56453782.html
- Xueqiu: https://xueqiu.com/2287778230/179182343
- AIM Group: https://aimgroup.com/2019/11/15/51job-backs-huali-university-cdp-holdings-in-mixed-q3/
- Statista: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1211995/china-leading-hiring-apps-based-on-monthly-active-users/
- Wikipedia: https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%89%8D%E7%A8%8B%E6%97%A0%E5%BF%A7#cite_note-7
58 (58同城 wǔbā tóngchéng)

Website:
Year Founded:
2005
Key Milestones / User and Growth Stats:
2005: Yao Jinbo founds 58.com in Beijing. He still serves as the CEO as of 2023.
2007: The company thrives via a simple classifieds model. Throughout the year it sets up office branches in Tianjin, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Guangzhou. The team builds out localized websites for more than 160 cities across the country.
2009: Registered users surpass 100 million!
2011: Chinese celebrity Yang Mi becomes the first celebrity spokesperson for 58.com – beginning a years-long relationship between the two. This event ushers in an era of massive marketing and national brand recognition for the platform.
2013: 58.com was officially listed on the New York Stock Exchange (symbol: ‘WUBA’), raising $187 million USD in the process.
2014: Strategic investments and acquisitions. In 2014, 58.com began deploying its capital in a significant way. Highlights for the year include investments in eDaijia (e代驾, Real Estate), Momo (陌陌, Social Media and Dating), Baojia (宝驾租车, Car Rental), and purchase of Charm 91 (购魅力91, Recruitment).
2015: Two giants merge (and more acquisitions).
- In April, 58.com announces a strategic investment and merger with Ganji, their biggest competitor and second-largest classifieds portal in China at the time. Founder CEO Yao Jinbo refers to the former rivalry between 58 and Ganji as “the most intense on the Internet.”
- Throughout the rest of the year, the newly formed 58 Group acquires other service giants Anjuke (安居客, Real Estate), ChinaHR (中华英才网, Human Resources), Jxedt.com (驾校一点通, Transportation and Licensing), and invests in Tubatu (土巴兔装修网, Home Decoration).
2018: In a widely promoted partnership, 58 launches its WeChat App and secures a $200 million USD investment from Tencent for its newly launched University-focused platform ZhuanZhuan (转转, Recruitment & Second-Hand Services).
The company reports adding 100 million users in 2018 alone.
2020: A group of investors including Warburg Pincus Asia LLC, General Atlantic Singapore Fund Pte Ltd, Ocean Link Partners Ltd, Founder/CEO Jinbo Yao, and Internet Opportunity Fund LP (an entity controlled by Yao) take 58 private off of the NYSE. The deal values the company at about $8.7 billion USD.
2022: The Ganji brand is changed from ‘Gangji Web’ (赶集网 Gǎnjí wǎng) to ‘Ganji Recruit’ (赶集直招 Gǎnjí zhí zhāo). The intent is to refocus the brand from general classifieds to recruitment and jobs.

References and Further Info:
- Our full article on 58: 58.com – ‘The Craigslist of China’
- Market Screener: https://www.marketscreener.com/quote/stock/51JOB-INC-9784/news/51job-Inc-acquired-Yingjiesheng-com-for-CNY-250-million-38283555/
- Seeking Alpha: https://seekingalpha.com/article/4350254-51job-despite-short-term-pain-long-run-perspectives-look-bright
- Crunchbase: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/51job
- China News: https://www.chinanews.com.cn/cj/2017/12-20/8405156.shtml
- Paul Weiss: https://www.paulweiss.com/practices/transactional/private-equity/news/dcp-capital-acquires-china-s-51job-in-take-private-deal-valued-at-43-billion?id=43047
- PRNewswire: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/51job-inc-announces-the-establishment-of-51job-university-56453782.html
- Xueqiu: https://xueqiu.com/2287778230/179182343
- AIM Group: https://aimgroup.com/2019/11/15/51job-backs-huali-university-cdp-holdings-in-mixed-q3/
- Statista: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1211995/china-leading-hiring-apps-based-on-monthly-active-users/
- Wikipedia: https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%89%8D%E7%A8%8B%E6%97%A0%E5%BF%A7#cite_note-7
BOSS Zhipin (BOSS直聘 BOSS zhí pìn)

Website:
Year Founded:
2014
Key Milestones:
2014: BOSS Zhipin was founded and launched its platform for part-time job seekers in China.
2015: Expanded to include full-time job postings and had over 1 million registered users.
2016: Raised $50 million in funding from investors and had over 10 million registered users.
2017: Had over 50 million registered users and was one of the top job search platforms in China.
2018: Named one of the “World’s Most Innovative Companies” by Fast Company, and its user base continued to grow rapidly.
2019: Hit over 100 million registered users and was the largest job search platform in China. Tencent leads a large round of funding (look up how much).
2020: BOSS Zhipin merged with Kanzhun, another Chinese HR company. The newly formed entity ‘Kanzhun Limited’ became one of the largest HR companies in the world.
2021: BOSS Zhipin reached over 200 million registered users and more than 10 million active job postings. In June 2021, Kanzhun Limited went public on the NASDAQ stock exchange of New York, raising $912 million USD.
2022: Kanzhun Limited listed on the Main Board of The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited.
User and Growth Stats:
BOSS Zhipin’s growth since launching has been nothing short of phenomenal. Since going public in 2021, the company has publicly filed key figures on their recent growth. Here a few of those highlights (in Chinese Yuan):
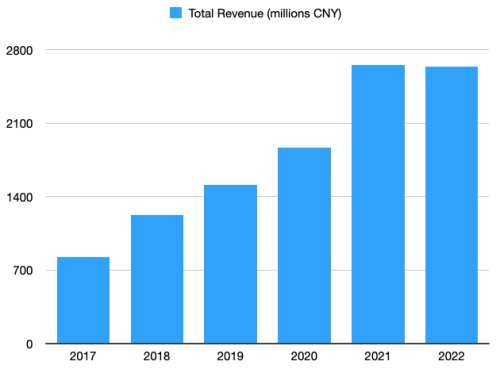
Annual Revenues have gone from 999 million in 2019 to 4.5 billion in 2022, about a 450% increase in just 3 years!
Monthly Active Users (MAU) have increased from 19.8 million in 2020 to 28.7 million in 2022, nearly a 45% increase in only 2 years.
Total paid enterprise customers have increased from 2.2 million in 2020 to 3.6 million in 2022, around a 64% increase in only 2 years.
Net income has gone from -502 million in 2019 to +107 million in 2022, making the company profitable on paper for the first time since reporting.

References and Further Info:
- Our full article on BOSS: BOSS Zhipin (BOSS直聘): The Most Active Job Portal in China
- Yahoo! Finance: https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/BZ?p=BZ
- Statista: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1211995/china-leading-hiring-apps-based-on-monthly-active-users/
- Bloomberg: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-06-11/kanzhun-soars-in-debut-after-top-of-range-912-million-u-s-ipo
- Crunchbase: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/bosszhipin
- FIFA: https://www.fifa.com/fifaplus/en/articles/boss-zhipin-signs-on-as-official-regional-supporter-of-fifa-world-cup-qatar
- Pymnts: https://www.pymnts.com/news/ipo/2021/chinese-online-recruiter-boss-zhipin-eyes-united-states-ipo/
- Pitchbook: https://pitchbook.com/profiles/company/166603-51
Ganji (赶集网 gǎnjí wǎng)

Website:
Year Founded:
2005
Key Milestones / User and Growth Stats:

References and Further Info:
- Our full article on Ganji: Ganji (赶集网): A Look at the Giant Chinese Classifieds Platform
- All other Ganji references have been linked to in the timeline above.
Lagou (拉勾 lā gōu)

Website:
Year Founded:
2013
Key Milestones / User and Growth Stats:
2013: Xu Dandan founds Lagou in Beijing. From the start, Lagou was positioned as a vertical recruitment platform for Internet talents. Referring to the target of tech talent with in-depth knowledge of certain skill sets, the founder said the company had a focus “One inch wide and one kilometer deep”.
2014: Funding rapid fire! Lagou has a BIG second year, convincing 3 sets of investors that it has a unique and valuable proposition in the Chinese HR landscape. It probably helped that the platform snagged over 1 million registered users in its first year of business!
- January 2014: Raises $330,00 USD from angel investors.
- March 2014: Raises $5,000,000 USD in series A.
- August 2014: Raises $25,000,000 in series B.
2015-2016: With a war chest of financing and connections, Lagou enters a stage of rapid growth and expansion. The firm sets up an education unit with the aim of providing quality training to make candidates “more valuable”.
- March 2016: Raises $34,000,000 USD in series C funding round. Qiming Venture Partners again joins this round after participating in series B.
2017: In September, the Chinese HR services company 51job acquired a controlling stake in Lagou, marking a significant development in the company’s history.
- September 2017: Raises $120,000,000 USD in series D funding.
2018: Reaches 1.2 million companies registered, 34 million job seekers registered. At this stage, the platform is receiving over 12 million job applications every month.
2019: The platform broadens its focus to cover various industries beyond just IT and technology.
2020: Lagou reaches over 25 million users.
2022: The company’s annual employment promotion following Chinese New Year hits record heights. During the promo, an average of 100 new jobs were posted every minute, and someone received an offer every 6 seconds!
2023: After 10 years, Founder & CEO Xu Dandan steps down. HR giant and controlling owner 51job takes over management.

References and Further Info:
- Our full article on Lagou: Lagou (拉勾): The Place for Tech Jobs
- INF: https://inf.news/en/economy/546af7fa2beebd0d2a11e3924e0d0565.html
- Crunchbase: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/lagou/company_overview/overview_timeline
- Staffing2Industry: https://www2.staffingindustry.com/row/Editorial/Daily-News/China-51job-announces-60-stake-in-online-recruitment-platform-Lagou-for-119-million-43507
- PR Newswire: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/51job-inc-announces-strategic-investment-in-lagou-300523401.html
- Baidu: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%8B%89%E5%8B%BE/50943161
Liepin (同道猎聘 tóngdào liè pìn)

Website:
Year Founded:
2011
Key Milestones:
2011: Liepin’s Founding
Liepin was founded in 2011 as an online platform dedicated to executive and professional recruitment. From the start, the company aimed to provide a specialized service for connecting top-level talent with job opportunities in China.
2014: Changed domain name from Lietou to Liepin
In January 2014, the domain name of Liepin.com was changed from lietou.com (猎头), a name synonymous with headhunting, to liepin.com (猎聘). This domain name change signifies that it will serve more professional managers and enterprises in addition to serving the headhunting industry.
2017: Acquisition of ChinaHR
Liepin acquired ChinaHR, another major Chinese job site, in 2017. This acquisition helped Liepin expand its user base, increase its market share, and further diversify its offerings in the recruitment industry.
2018: Collaboration with Tsinghua University
Liepin collaborated with Tsinghua University in 2018 to establish the Liepin-Tsinghua Talent Research Center. This collaboration aimed to conduct research on talent development, recruitment trends, and market insights to better serve the needs of job seekers and employers.
2018: Listing on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange
Wise Talent Information Technology, the parent company of Chinese executive headhunting platform Liepin.com, joined the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in June 2018.
2019: Launch of AI-Driven Solutions
Liepin introduced artificial intelligence (AI)-driven solutions to its platform in 2019. These AI technologies enhanced the matching process between job seekers and employers, improving efficiency and accuracy in the recruitment process.
2020: Tongdao Liepin Group
In June 2020, the parent entity was renamed “Tongdao Liepin Group” to express the company’s strategy of more diversified human resources services.

User and Growth Stats:
Liepin’s growth since launching in 2011 has been impressive and consistent. Since going public in 2018, the company has publicly filed key figures on their growth. Here a few of those highlights:
Annual Revenues reached RMB824.7 million (US$115,7 million) in 2017 after only 6 years of business! From 2017-2022 the company more than tripled their revenue, reaching RMB2,637.9 million (US$370.1 million).
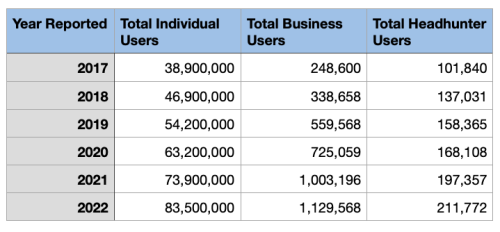
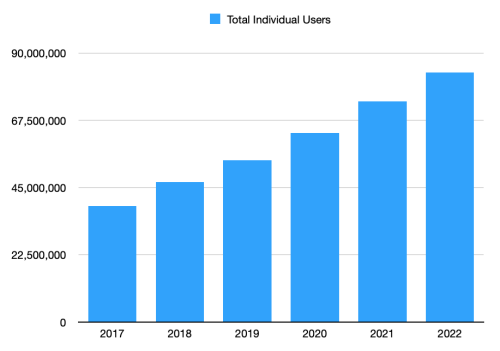
Total Individual Users reached 83.5 million by 2022.
Verified Business Users grew to 1,129,568 as of year end 2022.
Verified Headhunter Users grew to 211,772 by year end 2022.
References and Further Info:
- Our full article on Liepin: Liepin 猎聘: China’s Leading High-End Talent Platform
- Forbes: https://www.forbes.com/sites/russellflannery/2015/11/18/now-public-liepin-expects-to-fill-10-of-chinas-executive-job-placements/
- Crunchbase: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/liepin-com
- SCMP: https://www.scmp.com/business/companies/article/2151081/chinas-largest-job-site-liepin-seeks-us400-million-hong-kong
- iMedia: https://min.news/en/economy/b5b253ce1e0bad0f21b0ac694c0c4efa.html
- PanDaily: https://pandaily.com/headhunting-master-liepin-goes-public-in-hk/
Maimai (脉脉 mài mài)

Website:
Year Founded:
2013
Key Milestones:
- In October 2013, Maimai was officially launched by founders Lin Fan (林帆) and Huang Wei (黄威) in Beijing, China. The firm raises Series A financing from Wuyuan Venture Capital.
- In August 2014, Maimai raised Series B financing from IDG and Wuyuan Capital (again). This year also saw the company start to focus on professional social media in addition to job services.
- In December 2016, just over 3 years after launching, Maimai achieved break-even.
- In November 2017, the firm received Series C financing, led by DCM, with IDG Capital and Wuyuan Capital continuing to invest. In addition, China’s leading career platform Zhaopin Recruitment was introduced as a strategic investor.
- In April 2018, Maimai raised Series D financing from a group including DST, IDG Capital, Wuyuan Capital, and DCM. The round values the company at over $1 billion USD, rendering it a Unicorn.
- In April 2019, Maimai’s registered users exceeded 80 million. In December of the same year, the ‘Colleague Circle’ function was launched, allowing co-workers a platform to share and discuss their work and companies.
- In March 2022, the number of registered users reached 120 million. The ‘Company Review’ model is also launched this year, aiming to provide transparent reviews and feedback from current and former employees.

User Stats:
From Maimai’s Website:
“The Maimai platform has gathered a large number of ‘mid-to-high-end talents’.
Its users come from many Fortune 500 and China’s Fortune 500 companies, and are mainly urban workplace elites with high education and high income.
It currently covers IT Internet, artificial intelligence, new energy vehicles, chips, biomedicine, auditing, finance, cultural media, real estate, manufacturing, education and training and other industries.”
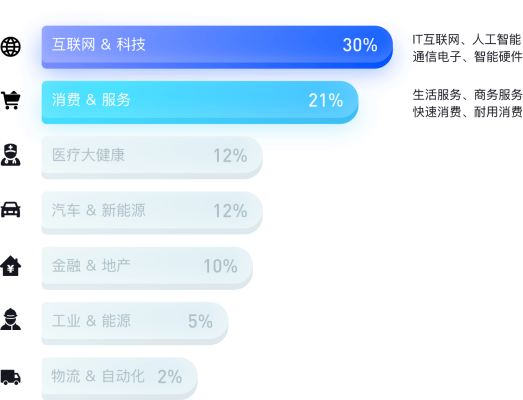
While Maimai covers nearly all industries, it’s focus on ‘mid-to-high-end talents’ does concentrate around a few key ones:
The ‘Internet & Technology’ and ‘Sales & Services’ industries cover 51% of Maimai users.
The ‘Medical & Health’, ‘Automotive’, and ‘Finance & Real Estate’ industries each make up a solid amount of users as well, coming in at 12%, 12%, and 10% of users respectively.
References and Further Info:
- Our full article on Maimai: Maimai (脉脉): The Closest Thing to LinkedIn in China
- All other Maimai references are directly from the company website, or have been linked to in the timeline above.
Zhilian Zhaopin (智联招聘 zhìlián zhāopìn)

Website:
Year Founded:
1997
Key Milestones:
1997: Founded in Beijing as an offline recruitment agency.
2004: Launches its online platform, allowing job seekers and employers to connect online.
2011: Acquired by SEEK, an Australian online recruitment company.
2014: Listed on the New York Stock Exchange, raising over $170 million in its initial public offering.
2015: Launches its mobile app, making it easier for job seekers to search for job postings on the go.
2017: Introduces AI-powered tools to help match job seekers with relevant job postings and improve the efficiency of the recruitment process.
2017: Hillhouse Capital, FountainVest Partners, and Seek International take Zhaopin private at a value of $1.01 billion USD.
2018: Partners with Tencent to expand its reach and improve its mobile offerings.
2020: Launches a series of online recruitment events in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing job seekers to connect with potential employers virtually.
2021: Announces plans to launch an online education platform, providing job seekers with access to career development resources and training.
2021: Changes ownership once again – a private consortium led by China-based Primavera Capital Group purchase the majority share of the company.

User & Growths Stats:
The company has quite the user base in China, here are a few highlights to that end:
- Over 200 million registered users as of 2021.
- Over 9 million average daily active users in 2020.
- Used by over 90% of the top 500 companies in China.
- Available in over 30 cities in China, including Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen.
2014: Reports over 60 million registered users.
2018: Reports over 160 million registered users and over 100 million monthly active users.
2020: Reports over 200 million registered users and over 120 million monthly active users.
References and Further Info:
- Our full article on Zhaopin: Zhilian Zhaopin (智联招聘): An Overview of the Chinese Job Platform
- Crunchbase: https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/zhaopin
- Pitchbook: https://pitchbook.com/newsletter/chinas-zhaopin-goes-public-on-nyse
- Seeking Alpha: https://seekingalpha.com/symbol/ZPIN/news
- ZoomInfo: https://www.zoominfo.com/c/zhaopin-ltd/43302973
- PRNewswire: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/zhaopins-china-employment-data-now-available-on-bloomberg-300394490.html
- Reuters: https://www.reuters.com/world/china/australias-seek-talks-cut-zhaopin-stake-makes-ex-cba-boss-narev-ceo-2021-02-23/
Table of Contents
ToggleHiring in China?
We can help, and likely lower your hiring costs by over 80%
Our China Candidate Sourcing service helps companies reach great talent across these leading Chinese job platforms. Contact us to discuss hiring goals, salary & compensation budgets, and if TeamedUp China is the right fit to support your organization.
Let’s find your next great China-based team member together.